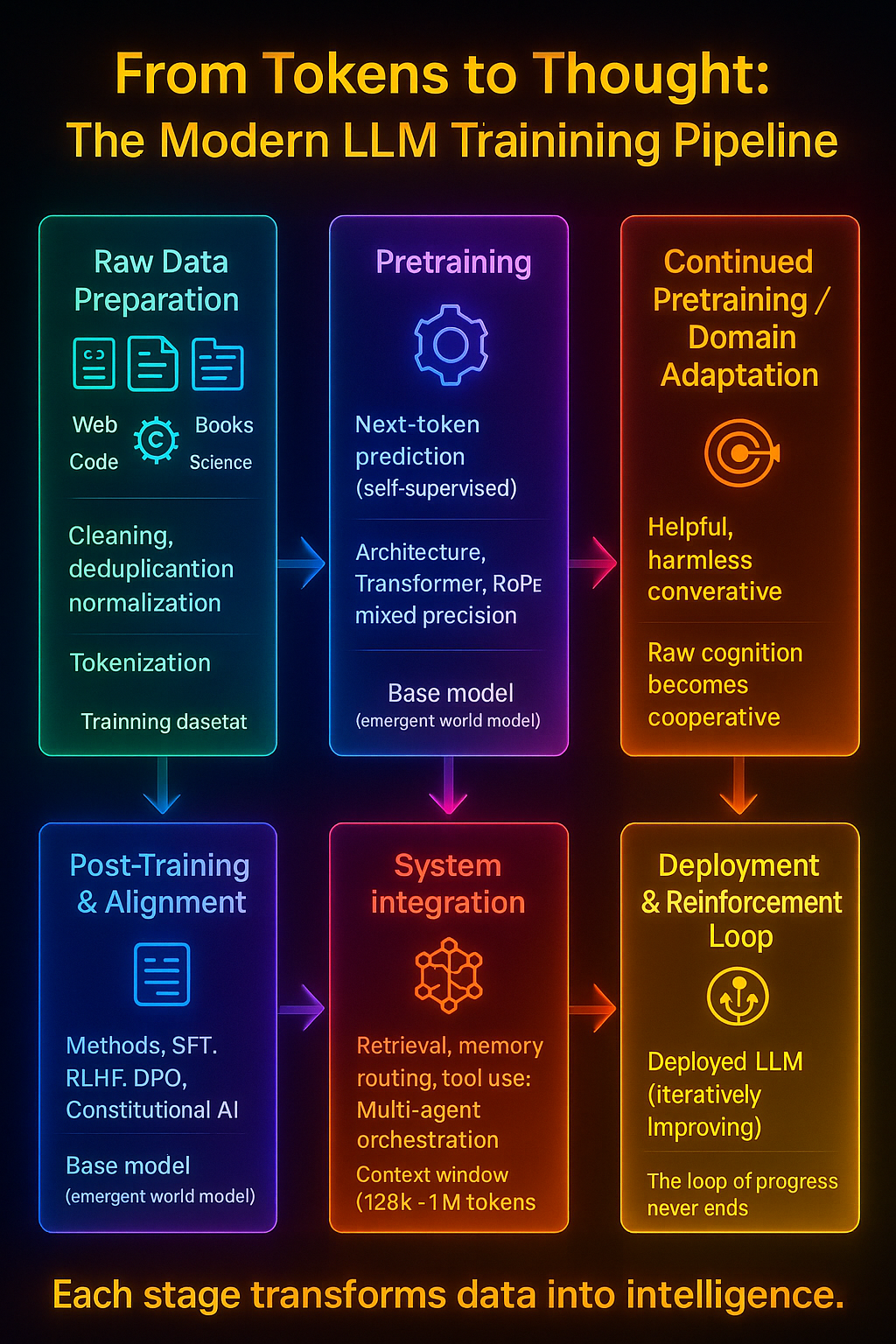
Raw Data Preparation {#raw-data-preparation}
Tokenization & Vocabulary Construction {#tokenization–vocabulary-construction}
Pretraining {#pretraining}
Continued Pretraining / Domain Adaptation {#continued-pretraining–domain-adaptation}
Post-Training (Alignment & RLHF) {#post-training-alignment–rlhf}
System Integration (Memory, Tools, and Reasoning) {#system-integration-memory-tools-and-reasoning}
Deployment & Reinforcement Loop {#deployment–reinforcement-loop}
1. Overview
Every major foundation model—GPT, Claude, Gemini, Llama, Mistral—passes through a three-phase evolution: pretraining, continued pretraining, and post-training. Each stage expands a model’s intelligence from pattern recognition to reasoning and alignment.
2. Stage 1 — Pretraining
Objective
Self-supervised learning on vast text corpora using the next-token prediction objective: [ L = - P(x_t | x_{<t}) ] The model learns to predict the next symbol in a sequence, which forces it to compress world-level regularities—language, logic, and cause-effect structure—into weights.
Data Scale
- Typical scale: 1–50 trillion tokens, drawn from filtered internet Natural langauge(web articles,books,academic papers),code,Mathematical equations, genetic code(genomes,DNA,RNA)
- Diversity is key: linguistic, cultural, and domain variety yields richer latent representations.
- Deduplication, normalization, and heuristic filters remove noise and contamination.
Architecture
- Transformer backbone (decoder-only or hybrid).
- Positional encodings (usually RoPE).
- Optimization with AdamW or Lion; mixed-precision training and distributed parallelism across thousands of GPUs.
Emergent Structure
As the model minimizes next-token loss, higher-order structure emerges: - Syntax → semantics → discourse → reasoning precursors - Implicit world models and factual recall - Token embeddings align semantically in latent space
Limitations
Pretraining teaches knowledge, not behavior. The model predicts patterns but has no understanding of correctness, safety, or user intent.
3. Stage 2 — Continued Pretraining / Domain Adaptation
After base training, models are often refined on curated corpora.
Goals
- Extend context window (e.g., 128k–1M tokens).
- Add specialized domains (code, math, scientific papers, multimodal data).
- Improve factual retention and robustness.
Techniques
- Continued next-token prediction on domain-specific data.
- Synthetic data augmentation (self-generated Q/A or dialogue).
- Mixture-of-Experts scaling to expand capacity without linear compute growth.
Outcome
This stage transforms a generic foundation model into a high-fidelity domain model—capable of reasoning in specific technical, legal, or creative contexts.
4. Stage 3 — Post-Training & Alignment
The final training layer converts the pretrained model into a useful, aligned assistant.
4.1 Instruction Tuning
Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on human-written instructions and responses. - Aligns model behavior to conversational and directive tasks. - Creates base “helpfulness and coherence” priors.
4.2 Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
A reward model ( R_) scores model outputs; policy optimization (PPO or DPO) adjusts weights to maximize human-preferred behavior.
Goal: Steer the model toward responses rated as truthful, harmless, and helpful.
4.3 Constitutional / Preference Optimization
Newer methods like Constitutional AI and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) remove the need for separate reward models by directly adjusting policy toward ranked preferences or textual constitutions.
4.4 Trade-off
Post-training sharpens helpfulness but can suppress raw capability if over-regularized. Precision alignment seeks balance—preserving deep reasoning while minimizing harmful outputs.
5. Stage 4 — System Integration
After post-training, models are embedded into ecosystems:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) – external memory through vector search.
- Tool Use – calling APIs, code execution, image generation.
- Memory Routing – dynamic recall of prior sessions or documents.
- Autonomy Layers – reasoning chains, planning blocks, or multi-agent frameworks.
This converts static models into dynamic reasoning systems.
6. Stage 5 — Frontier Trends
Modern research pushes each training stage further:
Curriculum Learning | Start with simple text → progressively complex reasoning tasks. | Improves stability and generalization. |
Active Learning | Query uncertain samples for human review. | Maximizes label efficiency. |
Long-Context Reinforcement | Rewards coherence across hundreds of thousands of tokens. | Enables multi-session memory. |
7. Closing Perspective
From pretraining to post-training, the process transforms raw pattern recognition into usable reasoning.
Continued Pretraining | Domain enrichment | Specialist foundation |
Post-Training | Human alignment | Conversational agent |
System Integration | Tool use & retrieval | Interactive reasoning engine |
Each phase stacks upon the last, evolving simple predictive learning into structured, aligned intelligence — the precursor to Super-LLMs.
“Training is not a single act — it is the shaping of cognition itself.”